Waves are associated to the transfer of energy as per we know. These are essential for transmitting energy in different forms. Numerous kind of waves are studies in physics. Requirements of medium for waves depends on types of waves, few waves needs material medium to propagate and few don’t need any medium propagate.
In this article, we’ll explain about the types of waves and difference between electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves in detail.
What are Waves?
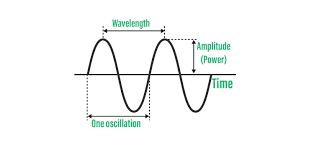
A wave is a rhythmic disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another without the movement of matter. Waves can travel by different medium such as air, water, and solids, while some waves, like electromagnetic waves, can travel by space without a medium.
Waves play a crucial part in daily life, from enabling sound and communication to facilitating vision and technological advancement. Whether its the sound of music, ocean waves, or the transmission of mobile signals, waves are an essential part of nature and modern science.
Examples of Waves
Waves are present in numerous aspects of our daily lives, transferring energy in different ways.
One common example is sound waves, which allows us to hear music, conversation, and other noises by vibrating air particles. Another familiar example is water waves, which we observe in oceans, lakes, and ponds when ripples forms due to wind or a disturbance like a stone being dropped into the water.
Light Waves: A type of electromagnetic wave, enable us to see the world around us, as sunlight and artificial lights travel in wave patterns.
Radia waves: These are used for wireless communication, allowing us to listen to the radio, use mobile phones, and access the internet by Wi-Fi.
In the medical field, X-rays and ultrasound waves help doctors examine bones and internal organs without surgery. Even natural disasters, like “Earthquakes”, produce seismic waves that travel through the earth surface, causing vibration and destruction.
From everyday sounds and vision to advanced technology, waves play an crucial role in communication, science, and nature.
Types of Waves in Physics
Waves in physics are classified into different types based on how they move and whether they need a medium to travel.
Below are the types of Waves
1. Mechanical Waves
- Surface waves: Surface waves are a combination of both transverse and longitudinal waves and travel along the interface between two different medium, such as waves and seismic surface waves.
- Transverse Waves: In transverse waves, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, as seen in the water and waves on a rope.
- Longitudinal Waves: In longitudinal waves, the particles move parallel to the wave direction, as in sound waves and seismic P-waves.
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared waves
- X-ray
- Ultraviolet rays
- Gamma rays
Difference Between Electromagnetic Waves and Mechanical Waves
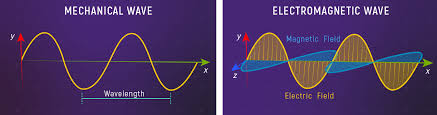
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves are two distinct types of waves that differ in their properties, behavior, and how they propagate.
- The key difference is that electromagnetic waves do not require a medium and can travel by a vacuum, while mechanical waves need a medium to propagate.
- Electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that travel perpendicular to each other and the wave direction. They Move at the speed of light and are crucial in communication, medical imaging, and energy transfer.
- In contrast, mechanical waves, including sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves, transfer energy by causing particles in a medium to vibrate. They can be transverse. Unlike electromagnetic waves, mechanical waves cannot travel by space.
Additionally, electromagnetic waves are self-propagating and can move through empty space, while mechanical waves rely on particle interaction in a medium. This fundamental different makes electromagnetic waves essential for space communication, while mechanical waves are important in natural phenomena like sound and earthquakes.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves differ primarily in their need for s medium and their propagation methods. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium and can travel through space, consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. They include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible lights, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays, which are widely used in communication, medical imaging, and technology.
In summary, electromagnetic waves are self-sustaining and can move through a vacuum, making them essential for wireless communication and spaces exploration, whereas mechanical waves rely on a physical medium, playing a vital role in sound, water movement, and seismic activates. Both types of waves are fundamental in daily life and technologies, each serving unique purposes based on their properties.
FAQs
can mechanical waves travel through vacuum?
What are the types of mechanical waves?
Following are three types:
- Surface waves: Surface waves are a combination of both transverse and longitudinal waves and travel along the interface between two different medium, such as waves and seismic surface waves.
- Transverse Waves: In transverse waves, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, as seen in the water and waves on a rope.
- Longitudinal Waves: In longitudinal waves, the particles move parallel to the wave direction, as in sound waves.
What are non-mechanical waves?
How you can define waves?
what are the types of waves?
Below are three types of Waves
- Mechanical Waves
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Matter Waves





